Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake: The Pros and Cons
Two terms you’re likely to come across in the crypto world are ‘proof of work’ and ‘proof of stake’, also known as PoW and PoS. What do they mean, and what’s the difference between Proof of Work and Proof of Stake? In this article, we’ll break it down.
PoW and PoS refer to different methods of verifying crypto transactions. These methods are known as ‘consensus mechanisms’ because they enable all network users to agree on whether or not a transaction is valid without the need for third-party intervention.
Consensus mechanisms are a key tool in the decentralised, user-led currency first envisaged by the creator of Bitcoin: the original cryptocurrency.
Cryptocurrency basics
To fully understand the difference between PoW vs PoS, it is necessary to explain how cryptocurrencies work.
All crypto transactions are recorded in a public ledger system known as a blockchain. Each transaction is organised into a new ‘block’ that contains verified details, including a timestamp, transaction data, and a cryptographic hash of the previous block.
Blocks are stored on the blockchain through cryptography, a system that ensures digital information is kept secure. It’s possible to interact and check the transactions of various blockchains, for example, you can use EtherScan to check what transactions are happening on the Ethereum blockchain.
Consensus mechanisms like PoW and PoS are tools used to verify transactions on the blockchain. In the next section, we’re going to look at PoW and PoS in a bit more detail.
What is Proof of Work (PoW)?

What is the Proof of Work crypto algorithm?
Proof of work (PoW) is a consensus mechanism used in cryptocurrency mining for validating transactions on the blockchain. It requires miners to solve mathematical problems using powerful computers. This increases the security of cryptocurrency by preventing anyone from gaming the system and, in return for their work, miners receive cryptocurrency tokens.
These computers, known as ‘miners’, must successfully solve these problems in order to create a new block and earn a miner’s reward. No new cryptographic problem is ever identical to another.
This means that when the problem is finally solved, the network knows that the transaction is authentic. At that point, the transaction is verified and the cryptocurrency amount in question is successfully moved to its new destination.
So, you might be wondering, is Bitcoin proof of work or stake? Bitcoin first introduced the use of PoW crypto algorithm to verify transactions in 2009. The creation of the PoW consensus algorithm was revolutionary. It proved vital in ensuring that the new cryptocurrency would be free of centralised control.
Proof of Work (PoW) Limitations
Although the PoW consensus mechanism has proven itself to be effective, it has some limitations, including:.
- Need for computing power: The PoW consensus algorithm relies heavily on powerful hardware to solve complex mathematical problems.
- High cost of setup: High computational power requires modern and expensive hardware.
- High energy consumption: A lot of computing power consumes a lot of energy.
- Requires heat management: To work effectively and prevent overheating, cooling systems need to be put in place for computer hardware.
- Lack of scalability: The infrastructure required is very expensive and hard to scale.
- The barrier to entry: Heavy computational requirements prevent a lot of individuals and organisations from participating in the consensus mechanism.
In addition, whenever a Bitcoin transaction is sent, it takes the network an average of 10 minutes to confirm it. Plus, the Bitcoin blockchain can only handle about seven transactions per second.
This has prompted a rise in transaction fees since the cryptocurrency was first established in 2009 and means transaction fees peak when the network is congested (meaning a lot of transactions are happening at once). Back in 2009, transaction fees cost a fraction of a cent, but as Bitcoin’s popularity grew, fees began to climb exponentially.
While Bitcoin excels in other areas, transaction fees on the Bitcoin network are still too high to make it suitable for small, everyday payments – and this problem is intrinsically tied to the PoW system.
The Lightning Network has provided an effective solution to this problem. This network is a payment protocol that works on top of the existing Bitcoin blockchain to enable faster, cheaper transactions among participating miners. Lightning Network transactions take under a minute and cost a fraction of a cent.
The biggest downside of PoW is that it uses vast amounts of computing power, and mining often requires highly specialised equipment that is unaffordable to average users. These factors have created pressure for an alternative consensus mechanism that is more environmentally friendly and easier for everyday users to benefit from.
What is Proof of Stake (PoS)?

What is the Proof of Stake (PoS) algorithm?
Proof of stake (PoS) is a consensus mechanism where new blocks on the blockchain are verified using validators instead of miners. Validators are cryptocurrency owners who “stake” their coins in a specialised wallet in exchange for a small reward based on the size of their “stake”. PoS is much more energy-efficient compared to PoW and has a lower barrier to entry.
Earlier this year, it was announced that Ethereum – the world’s second-most popular cryptocurrency – will move to a proof-of-stake model that could cut its energy usage by 99.5%.
The PoS model achieves consensus among users in a less labour-intensive way. While PoW rewards miners who solve complex equations, PoS decides which user will benefit from the next block’s rewards based on how much of the relevant cryptocurrency they have ‘staked’.
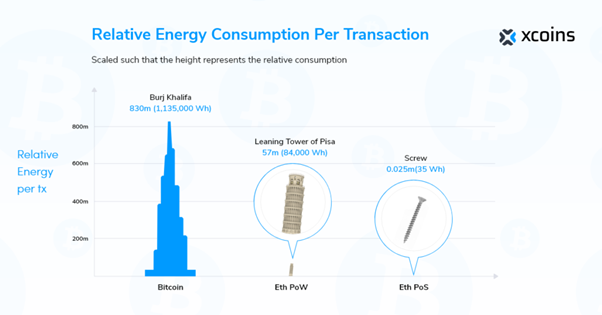
Bitcoin’s PoW energy consumption is visualised and compared to Eth’s PoW and estimated PoS energy consumption.
How the proof of stake (PoS) works
First of all, the user must put their cryptocurrency into a specific wallet. This wallet then ‘freezes’ the coins. This means that the coins are now being used to stake the network and cannot be spent or moved elsewhere until they are unstacked.
Blockchains that operate under a PoS model typically require a minimum amount of coins to be held in users’ wallets before they can start staking. This often requires a large upfront investment and is considered as one of the main limitations of PoS.
There are ways around this, however. For example, DeFi applications such as Lido allow users to pool their crypto to benefit from Ethereum 2.0 staking rewards without having to individually own high numbers of coins.
After you have staked coins, your chance of earning rewards is directly tied to the total percentage of coins you hold.
For example, if you stake 50 coins of a cryptocurrency that has 500 coins in circulation, you would then be holding 10% of the total coins in circulation and would have a 10% chance of winning every reward. In practice, users can expect a relatively reliable rate of return for staking coins if they pool their crypto with other users.
Benefits of Proof of Stake (PoS) system
PoS comes with its own set of limitations, but first, let’s take a look at the main advantages of the PoS protocol.
Energy efficiency
PoS is a more energy-efficient consensus mechanism because it takes much less computational power to hold and stake coins than to solve complex equations.
Honesty
Another argument in favour of the PoS mechanism is that those who stake their holdings will be motivated to keep the network secure by operating honestly. This is because if someone attempted to hack the network or process malicious transactions, users would lose their entire stake before the next block is created.

Abstract illustration of two blocks clashing in the midst of a blockchain network.
Proof of Stake (PoS) disadvantages
Even though PoS is far more energy-efficient than PoW, it is hard to ignore the biggest disadvantage of the PoS protocol.
Cost of winning the block reward
The more crypto a user stakes, the more likely they are to earn a reward when each new block is created. This means the more coins you can afford to buy, the more coins you can stake and gain. In short, users with more money to spend will always have a better chance of winning the reward, often making it an unequal system.
However, this problem also exists in the PoW system. The specialised equipment required to mine crypto is beyond the reach of most ordinary users but can be purchased in bulk by wealthy miners. Some organisations have been able to buy thousands of specialised devices to give them the greatest chance of earning rewards when a new block is created and this can lead to centralisation, something which is impossible under the PoS model.
Ultimately, it is hard to pinpoint which of the consensus algorithms is better, as both PoW and PoS have pros and cons. As individual users determine the fate of each cryptocurrency by voting with their feet, time will tell which system ends up being favoured on each blockchain.
Getting started with PoW and PoS
If you’re interested in becoming an early adopter of the PoS system, you first need to buy a supported cryptocurrency, for example, Ethereum (ETH).
Once you have the coins, head to one of the wallets that support staking and stake your cryptocurrency.
Once you’ve purchased the coins, you can become a validator. To get started, follow these steps:
- Firstly, make sure you meet all the requirements to become a validator. These will depend on the blockchain you want to stake on and they can be high. For example, to become a full validator on the Ethereum Blockchain, you will need 32 ETH. Remember that there are ways around this. DeFi apps such as Lido let users pool their Eth to stake without having to individually own a high number of coins.
- Find a suitable wallet to “stake” your cryptocurrency. You can see reccommendations for wallets that let you stake Ether on the official Ethereum Staking website, here.
- If you don’t want to or can’t become a full validator, you can join a staking pool such as RocketPool. A pool is where multiple crypto owners put their assets together to reach the minimum requirement, and share the reward based on their investment.
- Finally, deposit your purchased cryptocurrency to the desired pool or wallet and enjoy the rewards.
- Please read the documentation and requirements before depositing. In some cases (such as staking with Ethereum), you won’t be able to withdraw your assets until the staking period has finished.
To stay up to date on all things crypto, like Xcoins on Facebook, follow us on Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn, and sign up at the bottom of the page to subscribe.

