
Is ETH Becoming Truly Ultrasound Money?
The Merge has propelled Ethereum to become the number one hard-money currency worldwide by one key measure, overtaking Bitcoin in the eyes of many. We explain why this breakthrough is significant.
September 15th marked the end of an era for Ethereum, the world’s second-biggest crypto. After years of anticipation, the Merge went live and recent data shows that it’s already delivering on its promises.
Since its live date, we’ve seen a sharp drop in Ethereum’s net issuance rate (also known as inflation rate), suggesting that the crypto is well on its way to becoming deflationary.
In this article, we’ll break down why the change in Ethereum’s issuance rate is significant, the impact of the Merge, and what Ethereum’s future holds.
Ethereum is now created at a slower rate than Bitcoin
As of October 11th, Ethereum’s annualized net issuance rate sits at 0.09% – that’s according to data compiled by Ultra Sound Money that shows that only 8,030 new ETH have been added to the net supply since the Merge took place.
The net issuance rate, or inflation rate, figure is calculated by dividing Ethereum’s new supply by its existing supply. Prior to the Merge, Ethereum’s inflation rate was approximately 3.77%, meaning that it has decreased by roughly 3.68%.
In comparison, Ethereum’s biggest rival, Bitcoin, has an annualized issuance rate of approximately 1.87% based on data gathered by Messari.
This latest development means that Ethereum is now arguably more inflation-resistant than Bitcoin, the world’s biggest cryptocurrency commonly dubbed ‘digital gold’.
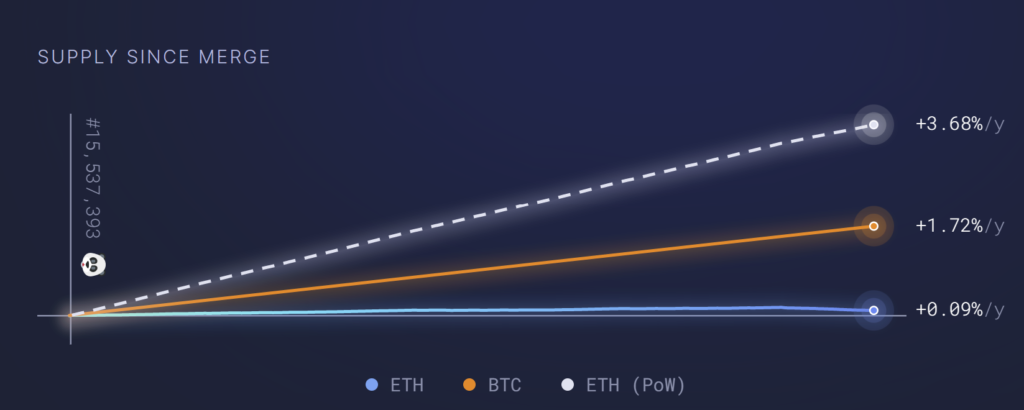
Ethereum’s inflation rate has fallen below Bitcoin’s following the Merge (Source: Ultra Sound Money, data from October 11th 2022).
Bitcoin has long held the attention of both crypto and traditional investors because of its scarcity and attractiveness as a store of value. However, the historic Merge upgrade has made Ethereum significantly more inflation-resistant, an attribute that’s most commonly ascribed to Bitcoin. As a result, the asset is garnering investors’ attention as “ultra-sound” currency, challenging both Bitcoin and conventional assets like gold.
The impact of the triple halving
There are three reasons for the dramatic reduction in Ethereum’s issuance rate. Firstly, the Merge marked Ethereum’s official transition from a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism to proof-of-stake (PoS). It’s estimated that by becoming a validator-secured network, Ethereum will reduce its energy consumption by up to 99%.
In addition to ending mining, the EIP-1559 mechanism has also reduced the ETH that goes into circulation by requiring that the network burns a proportion of transaction fees. These two factors, paired with the introduction of Ethereum staking, have caused the “triple halving” that slashed Ethereum’s inflation rate.

The Merge transitioned Ethereum from PoW to PoS, meaning that new ETH is no longer created through the energy-intensive process of mining.
Looking more closely at the numbers, Ethereum’s previous PoW network issued roughly 13,000 ETH in rewards to miners every day. But since the token-burning mechanism was introduced, and staking rewards were implemented, only around 1,600 ETH is dished out daily in rewards. According to the Ethereum Foundation, these changes have cut Ethereum’s daily issuance by 90%.
Ethereum eyes a deflationary future
It’s evident that the triple halving has positively affected Ethereum’s inflation rate, which has sparked a lot of interest and momentum around Ethereum as a long-term asset. This isn’t surprising, considering the current economic situation around the world.
With rampant inflation, rising prices, and incessant money-printing, Ethereum’s decreasing inflation rate demonstrates the value of Eth as an inflation hedge. It also positions the asset as an attractive way to store wealth, in a similar way that Bitcoin is viewed as digital gold.
Bitcoin’s annual issuance rate is now more than 10x higher than Ethereum’s following the Merge (Source: Messari).
If Ethereum does become completely deflationary, it will likely attract a lot more institutional investment over the next few years. This is just another reason why it’s becoming increasingly attractive to investors. This is evident from the fact that ETH is currently outperforming both BTC and the stock market.
Percentage change in the price of Ethereum in comparison to Bitcoin and the Nasdaq Composite.
In order for Ethereum to be considered deflationary, the network needs to issue fewer tokens than it burns every day, whether this happens will depend on the number of transactions on the network. If use of Ethereum continues to grow over time, we could indeed see Eth tip deflationary in the near future.
According to Ultra Sound Money, between September 26 and October 3, 466,000 ETH was burned while 603,000 new ETH was issued. Although Ethereum isn’t entirely deflationary yet, the Merge indicates that it’s not so far away, especially considering how far it’s come in the past couple of years.
If you’re considering purchasing Ethereum, at Xcoins, we offer 0% processing fees on your first verified purchase, and no verification when you buy up to $150 worth of crypto. Sign up now to benefit from buying crypto instantly and securely.
As always, this article does not constitute financial advice and you should be sure to do your own research and consult a professional financial advisor before making any investment decision.
To stay up to date on all things crypto, like Xcoins on Facebook, and follow us on Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn.

